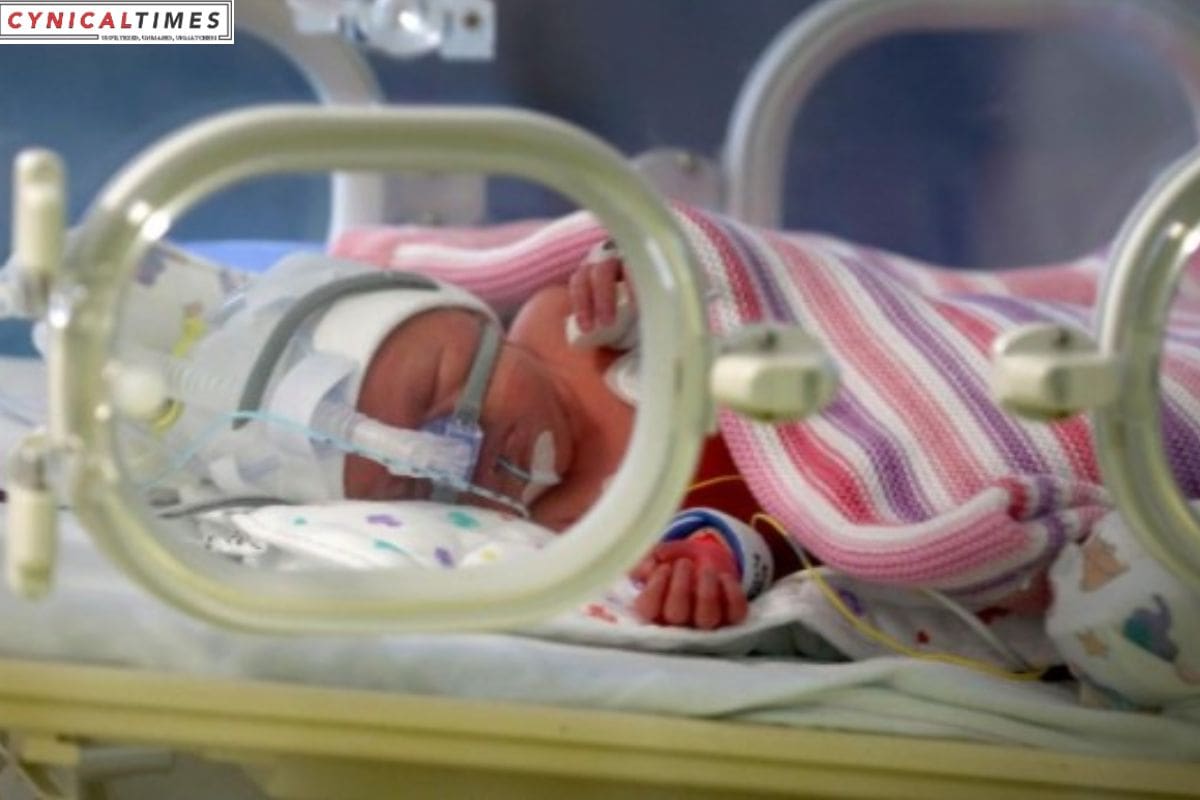
Artificial Wombs: Recently, the idea of a mechanical womb has become a medical possibility. FDA advisers discuss tech’s future.
An artificial womb aims to provide a womb-like environment for premature babies to grow. This idea seeks to address a vital issue in neonatal care: ensuring the survival and well-being of premature infants.
Babies born <37 weeks are preterm. They’re a health issue. The WHO says premature babies are the top cause of death for kids under 5. Premature babies may have health issues due to incomplete organ development, like the lungs and brain, which grow until late in pregnancy. These children may have long-term health issues such as breathing, stomach, vision, hearing problems, slow growth, or cerebral palsy.
In the US, preterm births are increasing. Per the CDC, preterm births rose from 10.1% in 2020 to 10.5% in 2021. This trend is most noticeable among African Americans, with a 50% higher rate of early parenthood than Whites and Hispanics.
Scientists and doctors study mechanical wombs as a solution. These gadgets don’t replace pregnancy. They save preemies born before 28 weeks. Less than 1% of kids are in this group.
When a baby is born, the younger it is, the higher the risk of death. Approximately 30% of babies at 22 weeks and 56% at 23 weeks survive. These numbers show the need for innovative support for children’s development.
Artificial wombs sustain a baby’s growth with air, food, and chemicals. They could solve a crucial part of baby care by doing that.
NICUs care for premature babies. In NICUs, babies get specialized care for eating, body temperature, and breathing, if needed. NICUs save lives but carry risks. Ventilation can harm preemies’ lungs.
FDA requires proof for robotic womb trials. Researchers must prove that these devices help infant growth and development, lower infant mortality rates, and surpass standard NICU care. Ethics, regulations, and health tracking are vital.
Scientists globally have tested ideas with animal models and artificial wombs. The study results are promising despite variations in tools and methods.
2017, doctors grew a lamb in a faux gut for 28 days. The lamb’s life was saved by a bag on its cord. The lamb’s organs changed. They said no life-threatening events were lasting. It was safe to go.
The University of Michigan tested fake placenta tech on lambs, and they survived for 16 days. The experiment showed lambs’ lung and brain growth, and they began automatic breathing. Researchers study artificial placenta as therapy for premature infants, addressing concerns.

ALSO READ: High Blood Pressure Warning: Global Crisis And Lifesaving Measures
Scientists in Japan and Australia kept a lamb alive for a week using a machine called EVE. Tech issues hurt the brain despite lung growth.
Researchers at Univ. of Toronto tested faux placenta with piglets. This showed heart and blood flow issues, emphasizing the difficulty of recreating the womb. Experts are hopeful about artificial wombs’ future despite concerns.
The following steps involve:
- Enhancing methods.
- Selecting appropriate animals for testing.
- Establishing ethical and legal frameworks for human studies.
“Viability” must change, especially for a baby’s survival outside the womb.
This tech raises concerns. Medical experts should discuss the risks, benefits, and unknowns of artificial womb ops with parents. More research is needed to assess treatment’s impact on children’s health.
As the FDA‘s advisory group investigates, it’s important to note that the agency will decide based on evidence and ethics. The meeting chooses the FDA regulation of artificial womb tech benefiting newborns.
Our Reader’s Queries
Are there artificial wombs?
Currently, studies on artificial wombs have solely been conducted on animals. However, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration recently convened to explore the possibility of utilizing artificial wombs, which were once considered a mere figment of imagination, to potentially aid premature infants in surviving. While the testing of such technology on humans remains a future prospect, this development marks a significant step forward in the field of neonatal care.
How long can you stay in artificial womb?
In 2016, researchers released two studies on the growth of human embryos in an ecto-uterine environment for thirteen days. However, the 14-day rule currently prohibits the extension of this period for artificial wombs.
Can a baby be grown in a lab?
Japanese scientists are confident that they can cultivate human babies in a laboratory. This development is reminiscent of the human cloning of Dolly the sheep, which occurred 20 to 30 years ago. The fertility industry is now experiencing similar advancements.
Can a baby grow outside the womb and survive?
Fetal viability is the ability of a baby to survive outside the womb. In the first trimester, viability is usually determined by the presence of a heartbeat on an ultrasound. Typically, a baby can survive outside the womb at around 22 weeks gestational age.