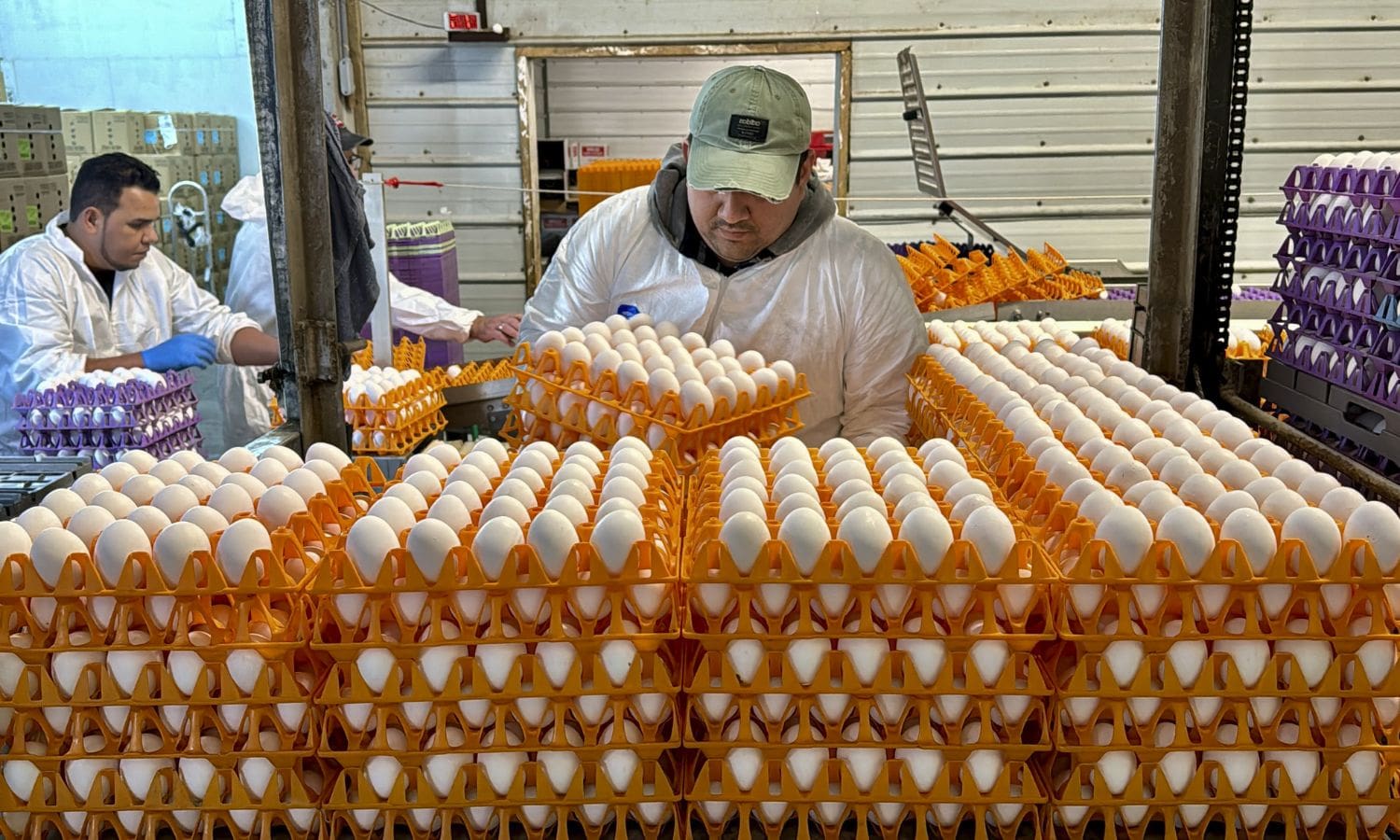
Avian Influenza Wreaks Havoc: The recent outbreak of Avian Influenza has sent shockwaves through the poultry industry in California, leaving farmers grappling with unprecedented challenges. What was initially thought to be a localized problem quickly escalated into a statewide crisis, with devastating consequences for poultry farms across the region.
This outbreak is not an isolated incident; it is part of a larger pattern that has plagued the industry for decades. As we examine the severity of the outbreak in California, explore its nationwide impact, and consider climate change as a contributing factor, it becomes clear that the ramifications extend far beyond the immediate concerns of poultry farmers.
The California poultry industry now faces a daunting task as it strives to recover from this crisis, while also addressing long-term challenges that threaten its survival.
Key Takeaways
- Outbreak severity: The avian influenza outbreak in California has resulted in the culling of over 1 million birds and the declaration of a state of emergency in Sonoma County. This highlights the seriousness of the situation and the impact it has had on poultry farms in the state.
- Climate change as a contributing factor: Altered weather patterns and changes in bird behavior due to climate change have increased the risks of avian influenza outbreaks. This emphasizes the broader environmental implications of the outbreak and the need to address climate change to prevent future outbreaks.
- Concerns in the California poultry industry: The outbreak has raised concerns about the spread of the virus within the poultry industry, particularly among backyard flock owners. Strict measures and collaboration between authorities, farmers, and backyard flock owners are necessary to prevent further spread and mitigate the economic impact on commercial farms.
- Recovery efforts and long-term challenges: Rebuilding flocks, implementing biosecurity measures, and investing in research and technology are crucial for the recovery of the poultry industry. Additionally, restoring consumer confidence, preventing future outbreaks, developing contingency plans, and adapting to changing regulations are long-term challenges that need to be addressed.
Outbreak Severity in California
The severity of the avian influenza outbreak in California is causing significant economic and agricultural repercussions, leading to the culling of over 1 million birds and prompting the state to declare a state of emergency in Sonoma County.

The highly pathogenic virus, transmitted by migratory birds, has particularly affected Sonoma County and Merced County. To contain the spread of the virus, commercial farms are implementing strict biosecurity measures, such as keeping flocks indoors until June.
The outbreak has resulted in hardships for farmers, workers, and consumers, with temporary surges in egg prices in the San Francisco Bay Area. The gravity of the situation is underscored by the state’s declaration of a state of emergency in Sonoma County.
The avian influenza outbreak in California is a significant concern that requires immediate attention and effective measures to mitigate its impact.
Nationwide Impact and Historical Context
Nationwide, the impact of the avian influenza outbreak on the poultry industry has been substantial, with record numbers of birds culled and significant economic repercussions. The ongoing situation has led to the culling of 82 million birds across 47 U.S. states, highlighting the persistent threat of avian influenza and the challenges faced by the poultry industry.
To better understand the nationwide impact and historical context of this outbreak, consider the following:
- Previous wave: A year ago, the poultry industry experienced a wave of bird flu outbreaks, resulting in record egg prices and shortages.
- Culling of birds: The current outbreak has necessitated the culling of unprecedented numbers of birds, affecting the supply of poultry products.
- Economic repercussions: The avian influenza outbreak has had significant economic consequences, impacting the livelihoods of poultry farmers and the overall industry.
- Nationwide spread: The outbreak has spread across 47 states, underscoring the widespread nature of the problem.
- Ongoing threat: The avian influenza poses a persistent threat to the poultry industry, requiring ongoing vigilance and preventive measures.
Climate Change as a Contributing Factor
Following the nationwide impact and historical context of the avian influenza outbreak, one crucial factor contributing to its occurrence is climate change, as experts point to altered weather patterns disrupting migratory bird patterns.
Climate change has been linked to increased risks of avian influenza outbreaks, highlighting the broader environmental implications and the role of climate factors in the emergence of such health crises.


Altered weather patterns, such as shifts in temperature and precipitation, can disrupt the seasonal migration patterns of birds. This disruption can lead to changes in bird behavior, including altered feeding and nesting grounds, which can increase the likelihood of contact between wild birds and domestic poultry.
As a result, the transmission of avian influenza viruses from wild birds to poultry is facilitated, posing significant challenges to poultry farms in California and beyond.
Concerns in the California Poultry Industry
With concerns growing over the potential transmission of avian flu from backyard chickens to commercial farms, the California poultry industry is facing significant challenges.
The following bullet points highlight some of the concerns in the industry:
- Strict measures advised for backyard flock owners, including wearing clean clothes and shoes to prevent contamination.
- Need for proactive measures to prevent the spread of the virus within the poultry industry.
- Potential economic impact on commercial farms due to outbreaks and loss of poultry.
- Increased pressure on biosecurity measures to protect poultry farms from infection.
- Collaboration between authorities, poultry farmers, and backyard flock owners to mitigate the risks and ensure the safety of the industry.
These concerns emphasize the critical importance of implementing proper biosecurity measures and maintaining strict protocols to prevent the spread of avian flu within the California poultry industry.
Recovery Efforts and Long-Term Challenges
The ongoing challenges faced by the California poultry industry in light of concerns over avian flu transmission highlight the pressing need for effective recovery efforts and strategies to address long-term challenges. Despite the setbacks caused by the outbreak, affected farms are actively working towards recovery. However, the road ahead is long, with the necessity to rebuild flocks and resume normal operations. This aspect underscores the resilience required within the poultry industry and the enduring impact of such outbreaks on the sector.
| Recovery Efforts | Long-Term Challenges |
|---|---|
| – Rebuilding flocks | – Restoring consumer confidence |
| – Implementing biosecurity measures | – Preventing future outbreaks |
| – Collaborating with government agencies and industry stakeholders | – Developing contingency plans |
| – Investing in research and technology | – Adapting to changing regulations |


Recovery efforts involve rebuilding flocks, implementing biosecurity measures, and collaborating with government agencies and industry stakeholders. Long-term challenges include restoring consumer confidence, preventing future outbreaks, developing contingency plans, and adapting to changing regulations. Investing in research and technology is essential for addressing these challenges and ensuring the sustainability of the poultry industry in California.
Conclusion Of Avian Influenza Wreaks Havoc
The avian influenza outbreak in California has had severe consequences for the poultry industry. Its nationwide impact and historical context highlight the need for effective measures to prevent and control future outbreaks.
Climate change is believed to be a contributing factor, adding to the concerns in the industry. Recovery efforts are underway, but long-term challenges remain.
It is crucial for policymakers and stakeholders to collaborate and implement strategies to mitigate the impact of avian influenza on poultry farms.
Our Reader’s Queries
Q1 What is the avian influenza virus in poultry?
A Avian influenza, commonly known as “bird flu,” is a respiratory illness affecting birds and caused by influenza A viruses. While wild birds, including ducks, gulls, and shorebirds, can carry and transmit these viruses without displaying symptoms, they pose a lethal threat to domestic poultry such as chickens, turkeys, ducks, and geese.
Q2 What birds are most at risk from avian flu?
A The assessed bird species predominantly comprise waterfowl (ducks, geese, swans), shorebirds (gulls, terns), and birds of prey (hawks, eagles, owls).
Q3 What is the most violent strain of avian influenza?
A H5N1, commonly known as “bird flu,” is recognized for its Asian-lineage HPAI H5N1 strain, responsible for a mortality rate of over 50% in humans infected by it. This strain has the capability to infect and cause fatalities in species that were previously not susceptible to influenza viruses, such as cats. Notably, it has demonstrated resilience even in the face of comprehensive poultry culling efforts.

